
Science Process
Proficiency Standards
 |
Science Process |
|
Proficiency Standards |
| Motion |
| How do things move? Packet |
 How do we describe motion? How do we describe motion? (Mastery) |
 How do I know if I’m moving? How do I know if I’m moving? (Interpersonal) |
 How do we describe different types of motion? How do we describe different types of motion?(Understanding) |
 How many ways can something move? How many ways can something move?(Self Expressive) |
|
Take every day before sleeping! Vocabulary Review Activities BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes |
Vocabulary Describing and Measuring Motion: Chapter 1 Section 1: Pages 14-27: Acceleration: Chapter 1 Section 3: Pages 34-38: Using Force and Motion- National Geographic Defining the Laws of Motion Investigating Forces And Motion Harcourt-Motion Booklet MotionAndMovement Booklet Science Skills Handbook Appendix: Pages 202-214: Process Skills Packet |
| Labs & Videos |
 |
 Motion Video Search |
 |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live Presentation Project Live Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
 |
An object is in motion when its distance or location from a reference point changes. |
 |
Average speed is: total distance in a given or total,
time. (Like from the start to finish line.) (The opposite is instantaneous speed, speed at a given moment in time like on a roller coaster.) Speed does not give a direction travelled. (Speed = Distance ÷ Time) |
 |
Acceleration is the rate
(how fast) at which velocity changes
|
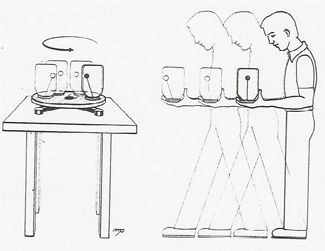 | An accelerometer measures changes in acceleration or jerk. Electronic acelerometers are used in cars to set off airbags and in runners' speedometers. |
 |
Velocity is speed in a given direction. |
 |
Vectors or rays are arrows that can show motion and forces. |
 |
Ways to describe motion with math include:
|
 |
Scientist Land speed record.: The science of aerodynamics and wheels. |
 |
Technology The wheel allows rotational motion to help move things with less friction. |